Windows 11 Haswell: Compatibility and Support Explained
7 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team Read more
Key notes
- Windows 11 has some compatibility issues with Haswell, but you still might be able to run it.
- The operating system supports only newer hardware, raising many compatibility concerns.
- Even if your hardware doesn't support the new version, you can always rely on virtualization software.

Windows 11 is finally here, but unfortunately, it seems that it won’t work with older devices, and this has many users worried.
To install the latest version, many users will be forced to upgrade their PC, or even buy a whole new computer, which is far from an optimal solution.
Microsoft decided to drop support for older hardware, and introduce the TPM requirement to boost the security of its users.
The new version has specific CPU requirements, and in today’s guide, we’re going to answer whether Windows 11 can work with Haswell processors.
Can I use Windows 11 and Haswell CPU?
What are Haswell CPUs?
Haswell CPUs are series is developed by Intel and released in 2013. These are 22nm processors, and they are designed to be optimized for power saving.
These models took many features from their predecessor, Ivy Bridge, but they also brought few new ones including support for new sockets, a wider core, improved performance, and new instructions.
The Haswell devices were a part of the fourth-generation core CPUs, but they were eventually replaced by Broadwell and Skylake models.
What are the Haswell CPU features?
The models from the Haswell series are the first desktop processors that were made for a system-on-chip architecture.
Regarding the thermal power design, these devices use 37-57W on laptops, 35-140W on desktops, and 11.5W-15W on the Ultrabook series.
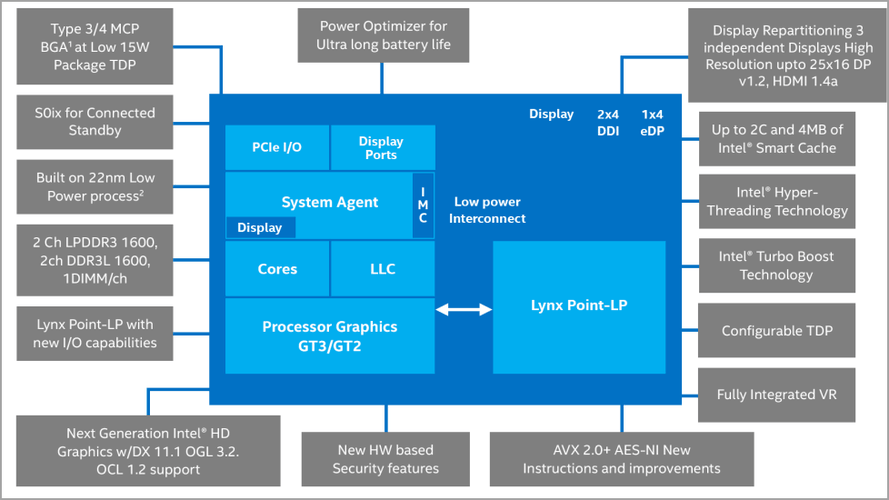
Haswell CPUs had support for dual-channel DDR3 memory with a maximum capacity of 32GB, at 1333MHz or 1600MHz frequency. As for PCI Express, there was support for 16 PCI Express 3.0 lanes.
Some models from this series came with Intel HD Graphics 5000, allowing users to enjoy multimedia.
As for the number of cores, here’s a quick overview:
- i7 – 4 cores and 8 threads
- i5 – 4 cores/threads
- i3 – 2 cores and 4 threads
- Pentium and Celecorn – 2cores/threads
In terms of CPU speed, high-end devices could reach 3.00GHz-4.00GHz, while mid-range ones would usually run on up to 2.0GHz-3.5GHz, and the entry models would run at 1.3GHz-2.6GHz.
For 2013 Haswell had great specs, so it’s no wonder that some users still use it on their older PCs. However, the question remains, how will Haswell work with Windows 11.
Does Windows 11 support Haswell processors?
Windows 11 requirements are different from the previous versions, and they have caused a bit of controversy.
The latest version will require a TPM chip, and if you’re not familiar with it, we suggest reading our TPM and Windows 11 guide for more information.
What about Haswell processors? According to Microsoft’s documentation, you’ll need at least an 8th generation Intel CPU, meaning Coffee Lake or newer.
If you’re using a 4th generation, such as Haswell, it means that you won’t be able to run Windows 11 since your hardware isn’t supported.
Even if you can’t upgrade, support for Windows 10 will last until 2025, so you can continue using it at least for few more years.
Why doesn’t Windows 11 support Haswell CPUs?
When Windows 11 was first announced, it was able to run on devices that don’t meet the hardware requirements fully, so if you had any version of the TPM, you could’ve installed it.
To learn more about different versions of this feature, check our TPM 1.2 vs TPM 2.0 guide for more in-depth information.
As you can see, Microsoft didn’t strictly enforce their requirements, and users were able to install Windows 11 with a warning message about using unsupported hardware.
That’s not the case anymore, and many older processors are unable to run the latest version of the operating system.

The reason behind this is most likely security, and many older CPUs don’t support TPM 2.0, which is required for Windows 11.
It’s worth mentioning that older processors don’t support certain security features, so they can’t utilize virtualization security and hypervisor-protected code integrity features that are always enabled.
Many are speculating that this is because of Spectre and Meltdown malware, and Intel’s 8th generation of CPU has improved security designed specifically to deal with this type of threat.
Take into consideration that the 8th generation is the minimum requirement for Windows 11, which leads us to believe that this is one of the reasons why Microsoft dropped support for older CPUs.
Is there any way to run Windows 11 on Haswell CPU?
Although Haswell devices aren’t officially supported, that hasn’t stopped users from installing the new operating system. It seems that Microsoft isn’t enforcing strict hardware requirements for Insider Program at the moment.
This allows you to join it and download Windows 11 on your PC with ease. However, this might change soon.
A couple of users reported that you can remove a hard drive that has an operating system installed and connect it to another PC, even if it doesn’t meet the hardware requirements, and it should work.
Keep in mind that this is just a workaround, and it might get patched in the future. For a long-term solution, you might want to run Windows 11 on a virtual machine.
Lastly, there’s an option to download Windows 11 ISO, and then modify it with files from the older version to circumvent hardware and security requirements.
This method might be risky especially when modifying ISO files, so we won’t go into detail, but it’s one method that advanced users might try.
Are Haswell processors good?
When they were released, they were great, but now, years after the initial release, they just can’t compete with modern low-end devices.
Haswell CPUs support only DDR3 at 1600MHz, which is a lot slower compared to newer models. However, these processors can still be used for basic needs, such as web browsing, office work, and light gaming.
What can I do if Windows 11 won’t work with my Haswell device?
Although there are still a couple of workarounds that allow you to install the latest version on devices that don’t meet the hardware requirements, we assume that Microsoft will put an end to that in near future.
This doesn’t leave users with many choices, and they will have to upgrade to meet the hardware requirements or purchase a Widows 11 ready PC.
Is Windows 11 worth upgrading to?
Yes, as long as your PC meets the hardware requirements. We wrote an in-depth guide in which we compared Windows 10 vs Windows 11, so be sure to check it out for more information.
The new version brings some major changes in terms of functionality and visual appearance, offering a complete visual revamp.
Performance-wise, Windows 11 will use DirectStorage that will improve gaming loading time and performance. On top of that, there’s improved security with the requirement of TPM and Secure Boot.
If your PC doesn’t meet the hardware requirements, you can continue using the current version of Windows, but keep in mind that many app and game developers will slowly drop support for it in the upcoming years.
Windows 11 doesn’t support Haswell CPUs officially, but there are few workarounds that you can try and see if they’ll help you run it.
Keep in mind that Microsoft is most likely aware of these workarounds and that they will most likely be disabled soon.
What are your thoughts on the new version of Windows and its CPU requirements and have you managed to run it on unsupported hardware? Let us know in the comments below.